Ray
Finding ray-object intersection and computing surface normal is central to ray tracing.
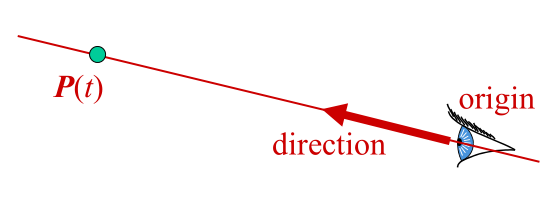
Ray representations:
- Two 3D vectors
- Ray origin position
- Ray direction vector
- Parametric form
- $P(t) = origin + t \times direction$
Computing Reflection / Refraction Rays
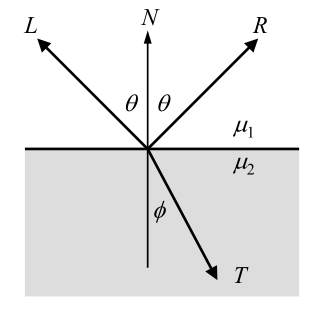
Snell’s law
Reflection
Refraction
Recursive Ray Tracing
For each reflection/refraction ray spawned, we can trace it just like tracing the original ray.
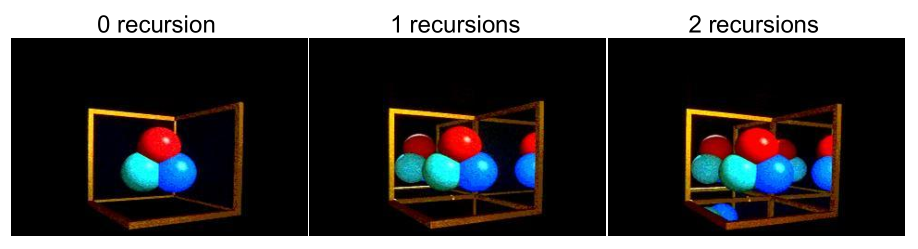
When to stop recursion?
- When the surface is totally diffuse (and opaque)
- When reflected/refracted ray hits nothing
- When maximum recursion depth is reached
- When the contribution of the reflected/refracted ray to thecolor at the top level is too small
- $(K_{rg1} | K_{tg1}) \times \cdots \times (k_{rg(n-1)}|k_{tg(n-1)}) < threshold $
Camera
Camera view & image resolution
- Camera position and orientation in world coordinate frame
- Similar to gluLookAt()
- Field of view
- Similar to gluPerspective(), but no need near & far plane
- Image resolution
- Number of pixels in each dimension
1 | Camera &Camera::setCamera( |